The journey of sperm is a testament to the remarkable complexity and resilience of life. By delving into the intricacies of sperm biology, we gain a deeper appreciation for the miraculous process of fertilization and the vital role that sperm play in the creation of new life.
Sperm
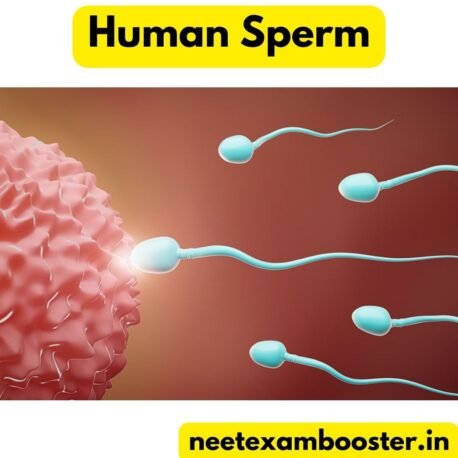
- Sperm are tiny cells produced by the male reproductive organs, made up of water, plasma, mucus, and small amounts of essential nutrients.
- On average, males produce millions of sperm cells daily, each containing 23 chromosomes.
- When a sperm fertilizes an egg, it results in an embryo cell with 46 chromosomes.
- A sperm cell typically consists of three parts: head, midsection, and tail.
- The sperm head contains chromatin (DNA material) and is covered by an acrosome, which has enzymes to help the sperm penetrate the egg.
- The midsection contains energy-producing mitochondria.
- The tail, the most complex structure, is involved in sperm movement.
- Sperm tails were once believed to sway like a snake, but recent studies show that sperm actually spin and drill into the surrounding fluid.
- Sperm morphology refers to the shape of sperm, including head size, DNA content, midpiece appearance, and tail structure.
- Abnormal sperm morphology, or teratozoospermia, can affect fertility as sperm need a specific shape to reach and penetrate the egg.
- Most men with abnormal sperm morphology can still father a child, but it may take longer or require assistance from a fertility specialist.




 155 out of 200 questions were directly asked from these notes in NEET 2024
155 out of 200 questions were directly asked from these notes in NEET 2024

Pingback: What is Genetic Engineering? - NEET EXAM BOOSTER