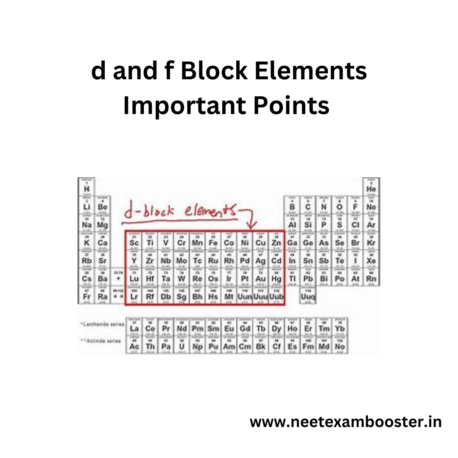
d and f block elements important points– The d-block elements, also known as the transition elements, occupy the middle portion of the periodic table and have partially filled d- orbitals. They exhibits a wide range of oxidation states, conductivity, and high melting and boiling points. Transition elements are known for their color and they act as catalysts. They form complex ions and show gradual changes in their properties across a period.
The f-block elements consist of lanthanides and actinides, which have partially filled f- orbitals. Lanthanides are similar and have various applications, while the actinides are radioactive and are used in nuclear reactions. Transition elements forms the coordination complexes, display magnetic properties, and have biological significance. They have smaller atomic radii but higher densities.
The f-block elements have complex electron configurations, filling the 4f and 5f orbitals. Overall, both d-block and f-block elements possess the unique characteristics that make them important in chemistry.
d and f block elements important points, d and f block elements important points, d and f block elements important points, d and f block elements important points, d and f block elements important points, d and f block elements important points, d and f block elements important points

NCERT Chemistry Class 12 Chapter 8- 25 d and f block elements important points
There are 25 important points on d-block and f-block elements –
- The d-block elements are also known as the transition elements, while the f-block elements are called as inner transition elements.
- Transition elements occupy the middle portion of periodic table, from groups 3 to 12.
- The f-block elements are located at the bottom of the periodic table, including lanthanides and actinides.
- Transition elements have partially filled d orbitals, while the inner transition elements have partially filled f orbitals.
- Transition elements exhibits a wide range of oxidation states due to availability of variable numbers of valence electrons.
- The transition elements are generally the good conductors of heat and electricity.
- These elements have high melting and boiling points compared to the s-block elements.
- Transition elements and their compounds often exhibits color due to presence of unpaired d electrons.
- Transition elements acts as catalysts in many chemical reactions.
- Many transition elements forms complex ions due to their ability to donate and accept the electrons.
- The f-block elements have two series: lanthanides (4f series) and actinides (5f series).
- Lanthanides are soft, silvery metals with the similar properties to each other.
- Actinides are the radioactive elements, and some of them are synthetic.
- Lanthanides are used in production of alloys, magnets, lasers, and phosphors.
- Actinides, such as uranium and plutonium, have applications in the nuclear reactors and weapons.
- Transition elements shows similarities in their chemical properties, and their properties change gradually as you move across a period.
- Transition elements forms the coordination complexes with ligands, which are molecules or ions that bond to a central metal ion.
- The magnetic properties of transition elements are influenced by presence of unpaired electrons.
- Transition elements shows a wide variety of colors in their compounds, such as the blue color of copper sulfate or the red color of chromium(III) chloride.
- Transition metal ions can form colored compounds with water, forming the hydrated metal ions.
- Some transition elements, like iron, are essential for the biological processes and are found in active sites of enzymes.
- The atomic radii of transition elements are smaller than those of the s-block elements but larger than those of the p-block elements.
- Transition elements often exhibits high densities due to their compact atomic arrangements.
- Some transition elements, such as gold and platinum, are highly valued for their rarity and the industrial applications.
- The f-block elements have more complex electronic configurations compared to the d-block elements, with electrons filling the 4f and 5f orbitals.
Some Important Questions From Biology Class 11
| Chapter Name | Quiz Link |
| The Living World | Play Now |
| Biological Classification | Play Now |
| Plant Kingdom | Play Now |
| Animal Kingdom | Play Now |
| Morphology of flowering plants | Play Now |
| Anatomy of flowering plants | Play Now |
| Cell: the unit of life | Play Now |
| Biomolecules | Play Now |
| Cell Cycle and cell division | Play Now |
| Transport in Plants | Play Now |
| Structural organisation in Animals | Play Now |
| Mineral nutrition | Play Now |
| Photosynthesis in higher plants | Play Now |
| Respiration in plants | Play Now |
| Plant Growth and development | Play Now |
| Digestion and Absorption | Play Now |
| Breathing and Exchange of Gases | Play Now |
| Body fluids and circulation | Play Now |
| Excretory products and their elimination | Play Now |
| Locomotion and Movement | Play Now |
| Neural Control and Coordination | Play Now |
| Chemical Coordination and Integration | Play Now |
Some Important Questions From Biology Class 12
| Chapter Name | Quiz Link |
| Reproduction in organism | Play Now |
| Sexual reproduction in flowering plant | Play Now |
| Human reproduction | Play Now |
| Reproductive health | Play Now |
| Principles of inheritance and variation | Play Now |
| Molecular basis of inheritance | Play Now |
| Evolution | Play Now |
| Human health and disease | Play Now |
| Strategies for enhancement in food product | Play Now |
| Microbes in human welfare | Play Now |
| Biotechnology principles and processes | Play Now |
| Biotechnology and its application | Play Now |
| Organism and population | Play Now |
| Ecosystem | Play Now |
| Biodiversity and its conservation | Play Now |
| Environment issue | Play Now |




 155 out of 200 questions were directly asked from these notes in NEET 2024
155 out of 200 questions were directly asked from these notes in NEET 2024
