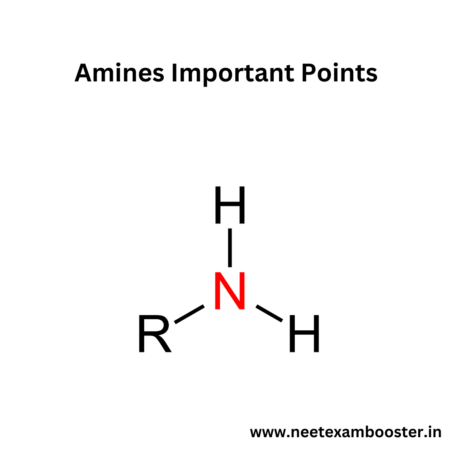
Amines important points – Amines are the organic compounds derived from ammonia, where one or more hydrogen atoms are replaced by the alkyl or aryl groups. They can be classified as the primary, secondary, or tertiary amines based on the number of attached groups.
Amines exhibit basic properties due to lone pair of electrons on the nitrogen atom, and they can act as bases and nucleophiles. They can undergo the various reactions such as alkylation, acylation, electrophilic aromatic substitution, oxidation, and amide formation. Amines have the higher boiling points and can form salts with the acids due to hydrogen bonding. They are utilized in synthesis of pharmaceuticals, dyes, pesticides, and other organic compounds, and they serve as ligands in coordination chemistry.
Amines also plays a role in important reactions like Hofmann degradation, Gabriel synthesis, reductive amination, and Hofmann rearrangement. Overall, amines are the versatile compounds with diverse applications in chemistry.
Amines important points, Amines important points, Amines important points, Amines important points, Amines important points, Amines important points, Amines important points, Amines important points, Amines important points

NCERT Chemistry Class 12 Chapter 13 – 25 Amines important points
There are 25 important points on Amines –
- Amines are the organic compounds that contain a nitrogen atom bonded to one or more alkyl or aryl groups.
- They are the derivatives of ammonia (NH3) where one or more hydrogen atoms are replaced by alkyl or aryl groups.
- Amines can be classified as primary (RNH2), secondary (R2NH), or tertiary (R3N), depending on number of alkyl or aryl groups attached to the nitrogen atom.
- Amines can be synthesized by reaction of ammonia with alkyl halides or aryl halides in a process known as nucleophilic substitution.
- Aromatic amines are a specific class of amines where nitrogen atom is bonded to an aromatic ring, such as aniline.
- Amines exhibits basic properties due to lone pair of electrons on the nitrogen atom, which can accept a proton.
- They can act as both bases and nucleophiles in the chemical reactions.
- Amines can undergo alkylation and acylation reactions, where the alkyl or acyl groups are added to the nitrogen atom.
- Aromatic amines can undergo the electrophilic aromatic substitution reactions.
- Amines can form salts with acids, such as ammonium chloride (NH4Cl), due to protonation of the nitrogen atom.
- Amines have the higher boiling points compared to hydrocarbons of similar molecular weight due to presence of hydrogen bonding between amine molecules.
- Amines can be used as solvents for polar substances due to their ability to form the hydrogen bonds.
- Amines can undergo the oxidation reactions to form amine oxides or nitroso compounds.
- Amines can be used as ligands in the coordination chemistry, forming complexes with metal ions.
- Amines can be converted into amides by the reaction with carboxylic acids or acid chlorides.
- Amines are widely used in synthesis of pharmaceuticals, dyes, pesticides, and many other organic compounds.
- Amines can act as the catalysts in various chemical reactions.
- Amines can undergo Hofmann degradation, where nitrogen atom is converted into an isocyanate by reaction with chlorine or bromine, followed by hydrolysis.
- Amines can undergo the Gabriel synthesis, which converts primary alkyl halides into primary amines using phthalimide as a starting material.
- Amines can form quaternary ammonium salts, where all the four substituents on nitrogen atom are alkyl or aryl groups.
- Amines can be protonated by the strong acids to form ammonium ions, which can be deprotonated by strong bases to regenerate amine.
- Amines can undergo the reductive amination, a reaction where a carbonyl compound reacts with an amine and a reducing agent to form an amine.
- Amines can be used as a chiral auxiliary groups in asymmetric synthesis.
- Amines can undergo the Hofmann rearrangement, a reaction where a primary amide is converted into a primary amine with one fewer carbon atom by treatment with the bromine and the aqueous base.
- Amines can participate in reactions such as Mannich reaction, Curtius rearrangement, and the reductive coupling reactions.
Some Important Questions From Biology Class 11
| Chapter Name | Quiz Link |
| The Living World | Play Now |
| Biological Classification | Play Now |
| Plant Kingdom | Play Now |
| Animal Kingdom | Play Now |
| Morphology of flowering plants | Play Now |
| Anatomy of flowering plants | Play Now |
| Cell: the unit of life | Play Now |
| Biomolecules | Play Now |
| Cell Cycle and cell division | Play Now |
| Transport in Plants | Play Now |
| Structural organisation in Animals | Play Now |
| Mineral nutrition | Play Now |
| Photosynthesis in higher plants | Play Now |
| Respiration in plants | Play Now |
| Plant Growth and development | Play Now |
| Digestion and Absorption | Play Now |
| Breathing and Exchange of Gases | Play Now |
| Body fluids and circulation | Play Now |
| Excretory products and their elimination | Play Now |
| Locomotion and Movement | Play Now |
| Neural Control and Coordination | Play Now |
| Chemical Coordination and Integration | Play Now |
Some Important Questions From Biology Class 12
| Chapter Name | Quiz Link |
| Reproduction in organism | Play Now |
| Sexual reproduction in flowering plant | Play Now |
| Human reproduction | Play Now |
| Reproductive health | Play Now |
| Principles of inheritance and variation | Play Now |
| Molecular basis of inheritance | Play Now |
| Evolution | Play Now |
| Human health and disease | Play Now |
| Strategies for enhancement in food product | Play Now |
| Microbes in human welfare | Play Now |
| Biotechnology principles and processes | Play Now |
| Biotechnology and its application | Play Now |
| Organism and population | Play Now |
| Ecosystem | Play Now |
| Biodiversity and its conservation | Play Now |
| Environment issue | Play Now |




 155 out of 200 questions were directly asked from these notes in NEET 2024
155 out of 200 questions were directly asked from these notes in NEET 2024

Pingback: Chemistry Important Points For NEET Class 12 - NCERT