Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic acids important points- Aldehydes, ketones, and carboxylic acids are important classes of the organic compounds. Aldehydes have a carbonyl group at the end of carbon chain, ketones have it in the middle, and carboxylic acids have it attached to a hydroxyl group. They are used as the solvents, reagents, and the starting materials in organic synthesis.
Aldehydes and ketones can undergo the nucleophilic addition reactions at the carbonyl carbon. Aldehydes can be oxidized obtain carboxylic acids, while ketones cannot. Tollen test distinguishes the aldehydes from ketones. They can be reduced to alcohols. Carboxylic acids can be reduced to primary alcohols and can be converted to acid chlorides. They undergo esterification with alcohols. Aldehydes and ketones react with various nucleophiles.
Acetal formation occurs the with alcohols and acid catalysts. They can undergo self-condensation reactions and oxidation. Carboxylic acids are weak acids, form salts, and can undergo neutralization. They have higher boiling points due to the hydrogen bonding. Aldehydes, ketones, and carboxylic acids have diverse applications in industries such as the pharmaceuticals, polymers, solvents, and perfumes.
Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic acids important point, Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic acids important points, Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic acids important points, Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic acids important points, Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic acids important points, Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic acids important points

NCERT Chemistry Class 12 Chapter 12 – 25 Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic acids important points
There are 25 important points on aldehydes Ketones and Carboxylic acids –
- Aldehydes, ketones, and carboxylic acids are the organic compounds containing a carbonyl group (C=O).
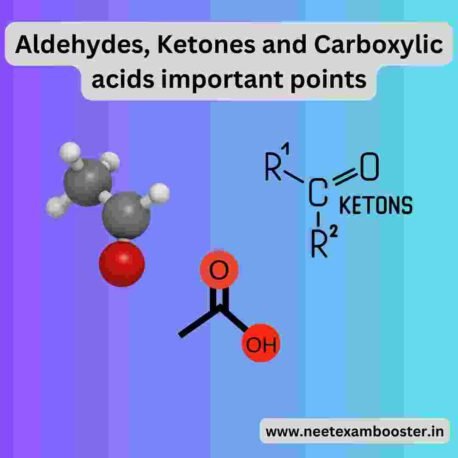
- Aldehydes have carbonyl group at the end of the carbon chain, while ketones have it in the middle.
- The carbonyl group in the carboxylic acids is attached to a hydroxyl group (-OH).
- Aldehydes and ketones are often used as the solvents, reagents, and starting materials in organic synthesis.
- Aldehydes and ketones are both named by replacing -e ending of the parent alkane with -al and -one, respectively.
- Carboxylic acids are named by replacing -e ending of the parent alkane with -oic acid.
- Aldehydes and ketones can undergo the nucleophilic addition reactions at the carbonyl carbon.
- The carbonyl carbon in aldehydes is more reactive than that in ketones due to absence of electron-donating alkyl groups.
- Aldehydes can be oxidized to carboxylic acids using the oxidizing agents such as potassium dichromate (K2Cr2O7) or Tollens’ reagent (ammoniacal silver nitrate).
- Tollen’s test is used to distinguish the aldehydes from ketones. Aldehydes give a positive silver mirror test, while ketones do not give.
- Both the aldehydes and ketones can undergo reduction to form alcohols using the reducing agents like sodium borohydride (NaBH4) or lithium aluminum hydride (LiAlH4).
- Carboxylic acids can be reduced to the primary alcohols using strong reducing agents such as lithium aluminum hydride (LiAlH4).
- Carboxylic acids can be converted to their corresponding acid chlorides by reacting with the thionyl chloride (SOCl2) or oxalyl chloride (COCl)2.
- The reaction between an alcohol and carboxylic acid leads to formation of an ester and water. This reaction is called as esterification.
- Aldehydes and ketones can undergo nucleophilic addition reactions with nucleophiles like Grignard reagents, hydrazines, and cyanide ions.
- Acetal formation occurs when the aldehydes or ketones react with alcohols in presence of an acid catalyst.
- Aldehydes and ketones can undergo the self-condensation reactions to form aldol products.
- The oxidation of the primary alcohols leads to the formation of aldehydes, while further oxidation of aldehydes results in the formation of carboxylic acids.
- The reduction of the carboxylic acids leads to the formation of the primary alcohols.
- Carboxylic acids are the weak acids and can undergo neutralization reactions with bases to form the salts.
- The acidity of the carboxylic acids is due to the resonance stabilization of resulting carboxylate anion.
- Carboxylic acids can form the intermolecular hydrogen bonds, resulting in higher boiling points compared to the aldehydes and ketones of similar molecular weight.
- The odor and flavor of many fruits and flowers are attributed to the volatile aldehydes and ketones.
- Carboxylic acids are commonly found in the vinegar, citrus fruits, and many other foods.
- Aldehydes and ketones are widely used in production of pharmaceuticals, polymers, solvents, and perfumes. Carboxylic acids are used in production of soaps, detergents, and food preservatives.
Some Important Questions From Biology Class 11
| Chapter Name | Quiz Link |
| The Living World | Play Now |
| Biological Classification | Play Now |
| Plant Kingdom | Play Now |
| Animal Kingdom | Play Now |
| Morphology of flowering plants | Play Now |
| Anatomy of flowering plants | Play Now |
| Cell: the unit of life | Play Now |
| Biomolecules | Play Now |
| Cell Cycle and cell division | Play Now |
| Transport in Plants | Play Now |
| Structural organisation in Animals | Play Now |
| Mineral nutrition | Play Now |
| Photosynthesis in higher plants | Play Now |
| Respiration in plants | Play Now |
| Plant Growth and development | Play Now |
| Digestion and Absorption | Play Now |
| Breathing and Exchange of Gases | Play Now |
| Body fluids and circulation | Play Now |
| Excretory products and their elimination | Play Now |
| Locomotion and Movement | Play Now |
| Neural Control and Coordination | Play Now |
| Chemical Coordination and Integration | Play Now |
Some Important Questions From Biology Class 12
| Chapter Name | Quiz Link |
| Reproduction in organism | Play Now |
| Sexual reproduction in flowering plant | Play Now |
| Human reproduction | Play Now |
| Reproductive health | Play Now |
| Principles of inheritance and variation | Play Now |
| Molecular basis of inheritance | Play Now |
| Evolution | Play Now |
| Human health and disease | Play Now |
| Strategies for enhancement in food product | Play Now |
| Microbes in human welfare | Play Now |
| Biotechnology principles and processes | Play Now |
| Biotechnology and its application | Play Now |
| Organism and population | Play Now |
| Ecosystem | Play Now |
| Biodiversity and its conservation | Play Now |
| Environment issue | Play Now |




 155 out of 200 questions were directly asked from these notes in NEET 2024
155 out of 200 questions were directly asked from these notes in NEET 2024
