Reproduction in Organism Class 12:- Reproduction is process in which new individuals of same species are produced by parents which carry an equal number of chromosomes from both parents. It is a fundamental feature due to which the organisms exists. Organisms reproduce in two ways:
1. Sexually
2.Asexually
Reproduction is an important phenomenon for all the known life on earth.
Important Questions Chapter 1 Reproduction in Organism Class 12

Reproduction in Organism Class 12 – Very Short Answer Types Questions
Q.1. What are two inherent characteristics of the amoeba and the yeast that favours asexual reproduction in them?
A.1. Two inherent properties of the amoeba that helps them to reproduce asexually are:
- They have the relatively simple structures and can divide very quickly.
- They are uniparental, because only one parent is involved.
Q.2. “The offsprings produced by the asexual reproduction are called clones”. Give reasons.
A.2. During the asexual reproduction, there is no fusion of the gametes and a single parent divides and redivides to produce offsprings. Hence, offsprings are morphologically and genetically similar to parents and therefore called clones.
Q.3. Why is the potato tuber is considered as a stem though it is an underground part? Give two reasons to support your answer?
A.3. Potato is referred to as the stem because:
- It has the nodes and the internodes.
- It can form plantlets from buds present over nodes.
Q.4. Among annual and perennial plants, which one has a shorter juvenile period. Explain and give reasons.
A.4. Entire life cycle of an annual plant has to be completed in one year which is shorter than the perennial plants.
Hence, it has the shorter juvenile period.
Q.5. Rearrange the following events in sequence in which they occur in sexual reproduction of the flowering plants: embryogenesis, fertilization, gametogenesis, pollination.
A.5. the order is as follows –
1.Pollination
2.Gametogenesis
3.Fertilization
4.Embryogenesis.
Q.6. How is it that the chances of the fruit set in a self-pollinated bisexual flower are far greater than a dioecious plant?
A.6. In bisexual flowers, anther and stigma lies close to each other. Thus, transfer of pollen to stigma is easier than the dioecious plants. However, in a dioecious plant, a pollinator is necessary to carry out the pollination process.
Therefore, chances of a fruit set in a self-pollinated bisexual flower are far greater than the dioecious plant.
Q.7. Is sexual reproduction hindered by presence of large number of the chromosomes in an organism? Explain.
A.7. No, the sexual reproduction is not hindered by a large number of the chromosomes in an organism. A fern Ophioglossum has 1260 number of chromosome and still reproduces sexually. Chromosomes are present within the nucleus of a cell. The chromosomes divides and segregates in this compartment irrespective of its number. It generates haploid gametes during the sexual reproduction.
Q.8. Explain your answer and give two examples if there is a relationship between size and lifespan of an organism.
A.8. No .There is no relationship between size and lifespan of an organism. For example –
- Size of a crow and a parrot is the same but a crow can live for 15 years while a parrot can live for 140 years.
- Mango tree and the banyan tree have same size but lifespan of a mango tree is shorter than that of the banyan tree.
Q.9. There are the two different types of flowers marked as A and B. Identify the flower types and the kind of pollination that will occur in each of flower –
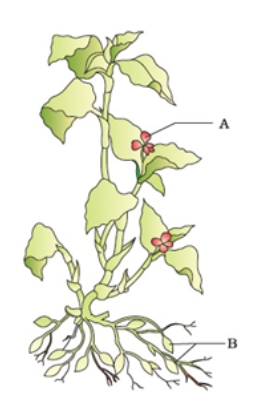
A.9. The two flowers are as follows –
A- Chasmogamous Flower (these remains open exposing anther and stigma to the environment).
B- Cleistogamous Flower (these remains closed) The type of pollination that will occur in the plant is Cleistogamy, a type of autogamy where plants possess both chasmogamous and cleistogamous flowers. In this, the chasmogamous flowers may undergo the self-pollination or the cross-pollination, and cleistogamous flowers may undergo only the self-pollination.
Q.10. Why multicellular organisms cannot reproduce by the process of cell division?
A.10. The cell division takes place in body of a multicellular organism but it does not aid in process of reproduction. Every day millions of the cells dies and are replaced by the other cells. Multicellular organisms have the well-developed reproductive organs that carries out the reproduction process.
Reproduction in Organism Class 12 Quiz
Q.11. Mark ovule and pericarp in below ffigure-

A.11.
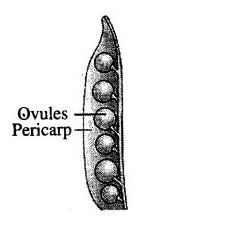
Q.12. Explain why gametes produced in the organisms in large numbers exhibits the external fertilization?
A.12. Producing a large number of gametes increases the chances of atleast one sperm fertilizing egg. Also, gametes released can be affected by predators and desiccation. That is why gametes produced in a large numbers exhibits the external fertilization.
Q.13. Identify monoecious and dioecious organisms from the following –
- The Earthworm
- The Chara
- The Marchantia
- The Cockroach
A.13.
1.Earthworm is Monoecious
2.Chara is Monoecious
3. Marchantia is Dioecious
4.Cockroach is Dioecious
Q.14. Match the following with the correct option –
| Column A | Column B |
| 1.Bryophyllum | 1.Offset |
| 2.Agave | 2.Eyes |
| 3.Potato | 3.Leaf Buds |
| 4.Water hyacinth | 4.Bulbils |
A.14. The correct matches are-
1.Bryophyllum-Leaf Buds
2. Agave- Bulbils
3.Potato- Eyes
4.Water hyacinth- Offset
Q.15. After the fertilization process, what do following parts of flowers grows into?
- The Ovary
- The Ovules
A.15.The Ovary grows into a fruit.
The Ovule grows into a seed.
Reproduction in Organism Class 12 – Short Answer Types Questions-
Q.1. Write the stage in life-cycle during the meiosis in haploid organisms that undergoes the sexual reproduction. Give reasons for this.
A.1. Meiosis takes place in diploid stage. This is because zygote is the only diploid cell in the life cycle of the haploid organisms.
Q.2. In the higher plants and the higher animals, number of taxa exhibiting the asexual reproduction is drastically reduced as compared to lower groups of the plants and the animals. Explain your answer.
A.2. Higher plants and animals have a complex structure as compared to lower plants and animals. They have well developed sexual reproductive organs in the body. They are structured to reproduce the sexually because of following reasons:
- To ensure the genetic recombination which results in the variation and gives rise to the evolution.
- Healthy progeny are being produced.
- Genetically different offsprings are being produced.
Q.3. Write the haploid and diploid individuals in family of honey bees and analyze the reasons behind their process of formation.
A.3. Sterile worker females are diploid.
fertile female queen bee is diploid. Male drones are haploid. Haploid and diploid individuals are formed both by the unfertilized and fertilized eggs, respectively. The fertilized eggs from female queen bee and the worker bees. Male drones are formed as a result of parthenogenesis, i.e., by the unfertilized eggs.
Q.4. Which type of reproduction is reduction division associated with? Give reasons to support your answer.
A.4. Reduction division is referred to as meiosis and is associated with the sexual reproduction. Reasons are as follows –
- The gametes that fuses should be haploid.
- The germ cells should be diploid. Meiosis can only reduce number into half.
Reproduction in Organism Class 12 study materials
Q.5. Is the vegetative propagation considered as a type of the asexual reproduction? Give reasons for your answer.
A.5. Yes, the vegetative propagation is a type of the asexual reproduction. This is because of the following reasons –
- The new individuals are produced by a single parent during the process.
- There is no fusion of the gametes.
- They are exact clones of their parents without any genetic or the morphological variations.
Q.6. Give reasons. Why the process of fertilization is not a compulsory event for production of fruits in some of the plants?
A.6. There are a few fruits such as the grapes, pomegranate, etc. developed from unfertilized ovaries. These are known as the parthenocarpic fruits.
The flowers of such plants are sprayed with a growth hormone that facilitates the fruit production even without the process of fertilization. But ovules do not change into the seeds.
Q.7. What will be consequences if the cell division is not followed by the cell differentiation in a developing embryo?
A.7. Cell division increases the number of the cells whereas cell differentiation helps in cell mass formation specialized tissues and organs. If the cell division is not followed by cell differentiation, there will be no embryo development and it will remain only as the mass of cell.
Q.8. What are changes that takes place in an angiosperm after the pollination and the fertilization have occurred?
A.8. The following are changes that occurs in an angiosperm after the pollination and the fertilization:
- Sepals, petals and the stamens falls off.
- Zygote is converted into an embryo.
- Embryo is present in ovule. The Ovule forms seed.
- The Ovary wall develops into the pericarp.
- Ovary forms fruit after fertilization.
Q.9. Explain why are seeds are scattered in juicy pulp of the tomato and arranged in a row in pea pod?
A.9. The pea plant is leguminous developed from the single carpel. When seeds mature, fruit splits into dorsal and ventral sides and discharges seeds. The plants which are developed from a single carpel have their ovules attached to ventral suture.
Therefore the fruit is developed with the marginal placentation and seeds are arranged in a row. On the contrary, tomato is a fleshy fruit developed from superior or the inferior ovary. Central chamber is divided into the compartments because the margins of carpels grow inward to the centre of ovary. The ovules are attached by placenta and are arranged radially on axis. That is why seeds are being scattered.
Q.10. Write the two differences and one similarity between the zoospore and the conidium. Draw diagrams of each of the following –
A.10.
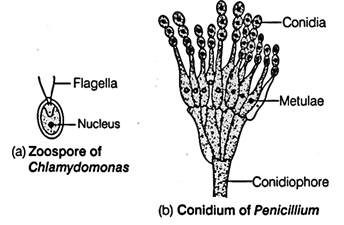
Differences:
| Zoospore | Conidium |
| 1.They are Flagellated. | 1.They are Non-flagellated. |
| 2. These are Endogenous, formed inside a sporangium. | 2. These are Exogenous, formed at tip of the conidiophores. |
Similarity- Both structures help in the asexual reproduction in organisms.
Q.11.What do u mean by Embryogenesis?
A.11. The Embryogenesis is the biological process by which embryo is formed and developed into a fetus.
Embryogenesis begins with fertilization of the ovum by the sperm.
Q.12.What do u mean by Fragmentation?
A.12. The Fragmentation is an asexual mode of reproduction. In this, the parent organism splits into the several parts and each part grows into the new individual.
For eg., Planaria are a group of free-living flatworms which reproduces their young ones through the process of Fragmentation.
Q.13.What do u mean by vegetative propagation?
A.13.Vegetative propagation is an asexual mode of reproduction occurring in the plants. This includes both the natural and the artificial method of the vegetative propagation
Q.14.What do u mean by Sexual Reproduction?
A.14. The sexual reproduction is a natural way of reproducing young ones which are identical to their parents.
In this type of reproduction, there is an involvement of both the parents. Sexual reproduction is observed only in multicellular organisms like animals, plants, mammals, humans, birds, etc.
Q.15.Define Gametogenesis?
A.15.Gametogenesis is the biological process by which diploid or the haploid cells undergoes cell division and the differentiation to form produce mature haploid gametes.
In human beings, during process of the gametogenesis the two different types of the gametes are present.
- Male gametes are known as the sperm.
- Female gametes are known as the ovum.
Q.16.What do you mean by bisexual flower?
A.16. A flower is a reproductive part of a plant.
Based on reproductive organs present in the flower, it is classified into two –
1. Bisexual Flower.
2. Unisexual flower.
The flower which includes both the male (androecium) and the female (gynoecium) reproductive organs are known as the bisexual flower. A bisexual flower is also known as a perfect flower.
Example of Bisexual flowers are -Lily, rose, and Hibiscus.
Q.17.What do u mean by Asexual Reproduction?
A.17. Asexual reproduction is another mode of reproducing their offsprings.
In this type of reproduction, there is an involvement of only one parent. Asexual reproduction is observed in both the multicellular and the unicellular organisms.
Q.18 Write the different types of asexual reproduction.
A.18.The different types of asexual reproduction are-
1. Budding
2. Binary fission
3. Fragmentation
4.Vegetative Propagation
5.Sporogenesis
Q.19.Write the complete process of the3 sexual reproduction?
A.19. Sexual reproduction includes the following set of events:
a)Pre-fertilization.
b)Fertilization.
c)Post-fertilization.
Reproduction in Organism Class 12 toppers notes
Q.20.Define the process of Pollination?
A.20. Pollination is a natural process of transferring the pollen grains from an anther ,the male part of a flower to the stigma , the female part of a flower.
There are the two types of pollination –
- Self-Pollination
- Cross-Pollination
Reproduction in Organism Class 12 – Long Answer Types Questions
Q.1. Write the differences between the sexual and the asexual reproduction. Explain the different types of asexual reproduction in the unicellular organisms.
A.1.
| Asexual Reproduction | Sexual Reproduction |
| 1.When offsprings are born without the contribution of the another organism of same species it is known as asexual reproduction. | 1.When offspring are born with help of another organism of same species but the opposite sex, it is known as sexual reproduction. |
| 2. The Organisms reproduce by the binary fission, fragmentation, budding, spore formation. | 2. The Organisms reproduces by syngamy and conjugation. |
| 3. They are Uniparental. | 3. They are Bi-parental. |
| 4.It divides by mitosis. | 4. It divides by mitosis and meiosis. |
| 5. The somatic cells are involved. | 5. The Germ cells are involved. |
| 6.Occurs in the unicellular organisms and lower invertebrates with the simple structures. | 6.Occurs in the higher plants and the animals. |
| 7.No fusion of the gametes takes place. | 7.fusion of the gametes takes place. |
| 8.Cells multiply rapidly in very less time. | 8. Sexual reproduction takes a longer time. |
| 9.No fertilization process takes place. | 9.Fertilization process takes place in process. |
The different types of the asexual reproduction in the organisms:
1.Binary fission
- It is common in the prokaryotes.
- living cell divides into the two daughter cells each containing a nucleus of its own.
- Daughter cells are exact copies of each other and parent cell.
- It is seen in the amoeba.
2.Budding
- A new organism grows from an outgrowth or a bud emerging from body of organism by process of the cell division.
- Outgrowth derives nutrition from mother and grows into a complete organism.
- It then detaches from mother and they lives individually. For example- hydra.
3.Fragmentation
If a part of an organism is cut and detached from organism it grows into an individual. For example- planaria.
Q.2. Write in brief the process of the gametogenesis in animals with suitable examples.
A.2. The biological process for the formation of the gametes, i.e., the production of sperms and oocytes known as gametogenesis.
The process for formation of the sperms is called as spermatogenesis and that for the oocytes is called as Oogenesis.
Spermatogenesis-
- Testosterone and the Follicle Stimulating Hormones,FSH are involved in process.
- Mitosis and the meiosis takes place in seminiferous tubules of testis which helps in formation of the spermatozoa.
- Spermatogonia undergoes the mitosis and produces diploid primary spermatocytes.
- Primary spermatocytes divides into the two secondary spermatocytes during first mitosis.
- Secondary spermatocytes further divides by the meiosis and forms the four spermatids.
- The spermatids differentiates into the functional sperms by a process known as the spermiogenesis.
Oogenesis-
- Estrogen, follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH),luteinizing hormone,LH and the progesterone are involved in the process.
- Primordial follicles of the ovaries transform into the oogonia and produces the diploid primary oocytes.
- Primary oocytes undergoes meiosis to form ootids. These get arrested at the prophase I stage of meiosis.
- On reaching the puberty, primary oocytes undergoes the meiosis and forms the haploid secondary oocytes and a polar body which disintegrates in later phase.
- The secondary oocytes get arrested the at metaphase II stage of meoisis 2.
- If egg gets fertilized, meiosis gets completed forming a polar body and an ootid.
- Ovum matures and polar bodies disintegrates.
Q.3. Differencentiate between:
- Oestrous cycle and menstrual cycle.
- Ovipary and vivipary.
A.3. 1.
| Oestrous Cycle | Menstrual Cycle |
| 1.Occurs in the non-primates such as the cows, dogs. | 1.Occurs in the primates such as the humans, monkeys, apes. |
| 2.Oestrous period is short in for example, it is 12-24 hours in case of cows. | 2.Cycle comprises of the menstrual phase, proliferative phase and secretory phase. |
| 3.Cycle does not involve blood flow. | 3. The blood flows in last few days of cycle. |
| 4. The broken endometrium is reabsorbed. | 4. The broken endometrium sheds during the menstruation. |
| 5.Copulation urge increases only during oestrous period. | 5.Copulation is not permitted by the females during menstrual phase. |
| Ovipary | Vivipary |
| 1.Animals lays the eggs. | 1.Animals gives the birth. |
| 2.Zygote develops outside body of the female. | 2.Zygote develops inside female reproductive tract. |
| 3.Eggs are laid in the water or moist land and chances of the survival are less. | 3.Chances of the survival of the newborn are more because it is developed insidefemale. |
Q.4. Rose plants have the large flowers but rarely do they produce the fruits. On contrary, the tomato plant produces the fruit but has a very small flowers. Comment your answer with suitable reasons.
A.4. The rose plants do not produce the fruits due to following reasons:
- No fertilization takes place in a rose flower due to absence of the viable pollen.
- Eggs produced are non-functional.
- These are self-incompatible.
- Ovule is defective and is non-functional.
- Since the rose plants reproduces vegetatively, they might be sterile in nature.
Q.5. Write important differences between the zoospore and the zygote.
A.5. The following are important differences between the zoospore and the zygote:
| Zoospore | Zygote |
| 1.The structure is associated with the asexual reproduction. | 1.The structure is associated with the sexual reproduction. |
| 2. These are thin-walled. | 2. These are thick-walled and helps to resist any damage and desiccation. |
| 3.It has flagella for the process of locomotion. | 3.It is non-motile, flagella are absent. |
| 4.It is formed during the favourable conditions and it germinates immediately. | 4.It undergoes a period of the dormancy in the algae and the fungi. |
Q.6. Write the post-fertilization changes that occur in case of the plants?
A.6. Post-fertilization changes that occur in the plants includes-
- Development of the Endosperm: Endosperm cell divides to form the triploid endosperm tissue. The cells have the reserve food material that provides the nutrition to developing embryo.
- Embryo’s Development: Zygote divides only after a certain amount of the endosperm is formed. The endosperm provides the nutrition for the development.
- Development of the seed: Ovule gets transformed into a seed after the double fertilization.
Fruit ‘s Formation: Fruits are formed by the cell division and the differentiation in ovary. The wall of ovary develops into walls of the fruit.
Click here to join our telegram channel for more important questions and answers like this Reproduction in Organism Class 12





 155 out of 200 questions were directly asked from these notes in NEET 2024
155 out of 200 questions were directly asked from these notes in NEET 2024
