Mineral Nutrition Class 11:- For all living organisms the basic essential requirements are same.The living organisms requires macromolecules such as carbohydrates, proteins,fats ,water and minerals.They help in growth and development.In living organisms

Mineral Nutrition Class 11 – Short Answer Type Questions
Q.1. Write the name of a plant which accumulates silicon.
A.1. Triticum aestivum and Oryza sativa accumulates silicon.
Q.2. How do living organisms in a mutualistic association give and take benefit from each other as seen in mycorrhiza?
A.2. Mycorrhiza is a symbiotic association between roots of vascular plants and fungus. This provides fungus with a constant supply of carbohydrates. Plants in return provide benefits of mycelium of fungus which promotes their absorptive capacity of minerals and water provides a large surface area of mycelium.
Q.3. Nitrogen fixation is observed only in prokaryotes and not in eukaryotes why?
A.3. Eukaryotes don’t contain enzyme – nitrogenase, required for fixing nitrogen which is possessed by prokaryotes such as Rhizobium.
Q.4. Write the name of nutrients obtained by carnivores plants such as venus flytrap and Nepenthes. From where do they obtain them ?
A.4. Both of them grow in nitrogen-deficient soil hence the make up for deficiency is by trapping insects for which they develop special adaptations.
Q.5. Write the name of a plant which lacks chlorophyll. How do they fulfil their nutritional requirements? Write an example.
A.5. Monotropa, commonly known as ghost plant, lacks chlorophyll.
Q.6. Give the name of an insectivorous angiosperm.
A.6. Dischidia is an insectivorous angiosperms.
Q.7. Write name of the mineral element that is restored with addition of Azotobacter culture to the soil.
A.7. To increase the nitrogen element in the maize field through nitrogen-fixation.
Q.8.What are the conditions posed by a leghaemoglobin in the root nodule of a leguminous plant ?
A.8.It is responsible for initiating anaerobic conditions in the root nodules. They serve as oxygen scavengers where they protect enzyme nitrogenase to come in contact with oxygen thus aiding in their proper functioning as nitrogen fixation.
Mineral Nutrition Class 11 Quiz
Q.9. On the basis of the mode of nutrition, what do following share in common?
Nepenthes, Drosera, Utricularia
A.9. They are carnivorous i.einsectivorous plants.
Q.10. Zinc-deficient plants exhibit reduced biosynthesis of which hormone?
A.10. Auxin hormone
Q.11. By which element deficiency occurs which is indicated by yellowish edges in leaves?
A.11. Deficiency of nitrogen indicates yellowish edges in leaves.
Q.12. Name the macronutrient which is a component of all organic compounds but is not obtained from the soil?
A.12. Carbon is a micronutrients which is a component of all organic compounds.
Q.13. Give name of one prokaryote which is non-symbiotic and fixes nitrogen.
A.13. Azotobacter is a prokaryote.
Q.14. Write the name of an important greenhouse gas produced by rice fields.
A.14. Methane is a important green house gas.
Q.15.Write the equation for reductive amination.

A.15.
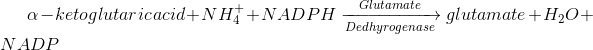
Q.16.Excess of Mn in soil lead to a deficiency of Ca, Mg and Fe Why?
A.16. Manganese becomes toxic when absorbed in higher amounts which is expressed in the form of brown spots surrounded by chlorotic veins. Due to
decline in uptake of iron and manganese.
They provide hinderance of binding of manganese enzyme to particular enzymes.
Also they provide hinderance of calcium translocation in shoot apex.
Therefore the excess of manganese causes lack of magnesium, calcium, and iron.
Mineral Nutrition Class 11 study materials
Mineral Nutrition Class 11 – Short Answer Type Questions
Q.1. Mention the importance of sulphur in plants. Write the name of amino acids which contain it.
A.1. Sulfur is works as an important macronutrient in plants which absorbed by the plants as an ion. Their primary functions is working as a component of proteins, vitamins(thiamine, biotin), coenzyme-A, amino acids (methionine, cysteine)…etc.It is also a necessary component of the ally sulphide (garlic, onion) and sinigrin(mustard). The deficiency of Sulfur can cause chlorosis in young leaves, formation of hard and woody stems, extensive root growth, etc. This also results in a reduction of juice content of citrus fruits and the yellow disease of tea. In amino acids methionine, cysteine, etc it is found.
Q.2.Write the significance role of the Pseudomonas and Thiobacillus in the nitrogen cycle?
A.2. The denitrifying bacteria which carry our denitrification in nitrogen cycle under the anaerobic conditions,the nitrate present in soil is reduced back to nitrogen oxides thereby they contributing to the atmospheric nitrogen.
Q.3. Observe the diagram and answer the following questions:
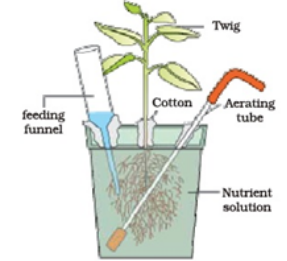
a) Write the name of the technique demonstrated in figure.Write the name of the scientist who demonstrated it for the first time.
b) Make a list of any three plants on which this technique can be applied for commercial purposes.
c) What is the importane role of feeding funnel and aerating tube?
A.3. a) The given technique is Hydroponics. The name of Scientist is – Julius Von Sachs
b) Following are the name of plants:
Hibiscus asculentus (ladies finger) Solanum Lycopersicum (tomato) Solanum melongena (brinjal)
c) The Feeding funnel is used to add nutrients and water in roots of plants. The aerating tube supplies oxygen for proper growth and development of roots nurturing in liquid solution.
Q.4. Write the name of the most important enzyme present in root nodules for nitrogen fixation? For nitrogen fixation, does it require the pink coloured pigment? Describe.
A.4. Nitrogenase enzyme is the most important enzyme present in root nodules for nitrogen fixation which catalyzes the conversion of atmospheric nitrogen to ammonia. The Leghaemoglobin is pink coloured pigment. It is required as it creates the anaerobic conditions for the functioning of the nitrogenase enzyme.
Q.5. Describe the given one with an example – that Carnivorous plants exhibit nutritional adaptation.
A.5. Carnivorous or insectivorous plants are commonly found in nitrogen deficient soil. For the makeup to this deficiency, they develope an insect trapping mechanism in which the leaves adapt to shape of a pitcher with the presence of insect digesting proteolytic enzymes.And they absorb nitrogen received from them and they trap insects.
Mineral Nutrition Class 11 – Long Answer Type Questions
Q.1. Write the essential elements for plants.Give the criteria for their essentiality. Write the classification of minerals basis the amount in which they are required by plants.
A.1. An element is said to be as an essential elements to a plant if it is required for maintaining the normal growth and reproduction of the plants. The requirement needs to be specific and can’t be replaced by any other element in the soil and they are directly involved in plant metabolism. Following are the given criteria for essentiality:
- In the deficiency of the element plant completes its life cycle and they areincapable to grow normally.
- The element can’t be substituted by another element and they are specific.
- For the plant metabolism the elements are very important.
Essential elements are furtherly subdivided into:
Macro elements – By plants it required in larger quantities, they are H, O, N, Mg, Ca and S.
Microelements – By plants it required in very trace or very low quantity they are Zn, Cu, Mo, Cl, Fe.
Mineral Nutrition Class 11 books
Q.2. What is the benefits of plants if they are supplied with excess nutrients?Give the reason if no, why and if yes, how?
A.2. No, this is not beneficial as the higher doses of micronutrients may become toxic or poisonous.The Toxic concentration is the any concentration that reduces dry weight of the tissue by 10%. However, the critical concentration is different for various micronutrients and for different plants. For any instance, beyond 600μ is very toxic for soybean and beyond 5300 μ very toxic for sunflower. The toxic effects can be due to the interference in absorption and proper functioning of nutrients or due to the excess amount of the micronutrient. Example – Toxicity in manganese can be due to:
The uptake of iron and magnesium
decrease in Hindrance of calcium and the translocation into shoot apex.
Q.3.Why to grow plants most of the crops are still cultivated on land despite hydroponics being a successful technique?
A.3. Hydroponics is a solution culture in which we raise plants in a soilless medium or condition.There are some disadvantages of these techniques, such as:
- Plants required regular root aeriation for normal growth.
- For the maximum growth,solution needs frequently replaced.
- The undesirable pH changes due to loss of certain ions which get quickly absorbed.
- This is an expensive technique.
- These methods may spreads water-borne diseases.
- Due to lack of knowledge and education, this is not practised by traditional farmers.
Q.4. Which are the essential elements? Describe macroelements and microelements with an examples.
A.4.The Roots are underground part of all the vascular plants and they are mainly responsible for the absorption of the chemical present in their surrounding soil. Among all available elements their are only 14 of the absorbed elements necessary for plant growth and they are called as the essential elements. They are required in larger amounts and are known as the macronutrients. Those essential elements which are required in lesser amounts are known as micronutrients.
The Macronutrients are getting absorbed from both air and soil. They include calcium, carbon, hydrogen, magnesium, nitrogen, oxygen, potassium, phosphorus, and sulfur etc.
The Macronutrients are absorbed from soil. They include iron, boron, chlorine, manganese, zinc, copper, molybdenum, and nickel etc.
Click here to join our telegram channel for more important questions like Mineral Nutrition Class 11





 155 out of 200 questions were directly asked from these notes in NEET 2024
155 out of 200 questions were directly asked from these notes in NEET 2024
