Heterocyst:- This article illuminates the unique structure and function of heterocysts, exploring their role in enabling cyanobacteria to thrive in diverse environments. Delve into the biochemical processes underlying nitrogen fixation within these cells, shedding light on their crucial contribution to ecosystem nitrogen cycling. Through comprehensive insights, readers will grasp the significance of heterocysts in sustaining life on Earth and their potential implications for agricultural and environmental practices. Unravel the mysteries of heterocysts and uncover their profound impact on our planet’s ecological balance.
Heterocyst
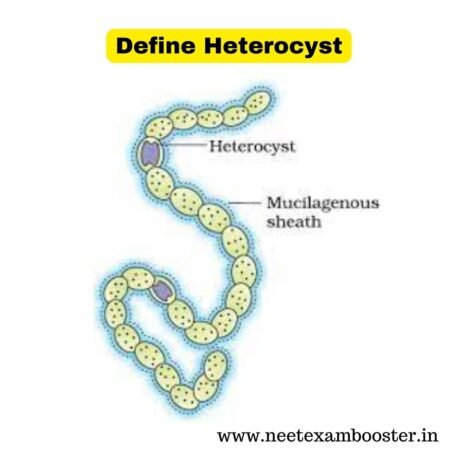
- Heterocyst is a specialized structure found in filamentous cyanobacteria, also known as blue-green algae.
- The function of heterocyst is nitrogen fixation.
- Heterocyst is thick and pale yellow in color.
- It has an extra cell wall layer, making it distinct from other cells in the filament.
- Heterocyst is usually found in an intercalary position, meaning it is located between two vegetative cells in the filament.
- In some cases, heterocyst can be found at the end of the filament.
- Heterocyst is a unique feature of cyanobacteria, as it is only found in this type of bacteria.




 155 out of 200 questions were directly asked from these notes in NEET 2024
155 out of 200 questions were directly asked from these notes in NEET 2024
